Blocked Tear Duct Treatment
Blocked Tear Duct Surgery opens obstructed tear ducts.
Find, compare and book Blocked Tear Duct Treatment from the best Private Provider near you. Search for Blocked Tear Duct Treatment or select from the menu, and book Blocked Tear Duct Treatment online now.
Blocked Tear Duct Treatment
Understanding Blocked Tear Ducts
Tear ducts, or nasolacrimal ducts, play a crucial role in eye health by draining excess tears from the eye into the nose. When these ducts become obstructed, it can lead to excessive tearing, discharge, and increased susceptibility to eye infections.
When Does Blocked Tear Duct Surgery Become Necessary
Blocked tear ducts can be caused by a variety of factors, including anatomical problems present at birth, chronic nasal and sinus inflammation, obstruction from a tumour, trauma to the nose, or conjunctivitis. When less invasive treatments such as warm compresses, massage, antibiotics, or dilation of the nasolacrimal duct fail to alleviate symptoms, or if the symptoms are severe, blocked tear duct surgery, or dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), may be recommended.
Overview of Blocked Tear Duct Surgery
Blocked tear duct surgery involves creating a new pathway for tears to drain from the eye into the nose, bypassing the blocked tear duct. This can be achieved through an external DCR, where a small incision is made on the side of the nose, or an endoscopic DCR, performed through the nose without leaving a skin incision. Both methods are equally successful and involve the placement of a temporary, flexible tube to keep the new duct open as it heals.
Book Now

Blocked Tear Duct Surgery
Blocked Tear Duct Surgery
Key takeways
- Blocked tear ducts can cause excessive tearing, discharge, and increased susceptibility to eye infections.
- Blocked tear duct surgery, or dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), is recommended when less invasive treatments fail or symptoms are severe.
- The surgery involves creating a new pathway for tears to drain from the eye into the nose, bypassing the blocked tear duct.
- Costs for the procedure can vary, and most health insurance plans cover the surgery if it's deemed medically necessary.
- Recovery from blocked tear duct surgery is typically comfortable, with minor bruising or swelling resolving over the first few weeks.
Common Symptoms and Conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a blocked tear duct?
A blocked tear duct, or nasolacrimal duct obstruction, is a condition where the duct that normally allows tears to drain from the eyes into the nose is obstructed. This can lead to symptoms such as excessive tearing, discharge, and increased susceptibility to eye infections.
What causes blocked tear ducts?
Blocked tear ducts can be caused by a variety of factors, including anatomical problems present at birth, chronic nasal and sinus inflammation, obstruction from a tumour, trauma to the nose, or conjunctivitis.
What is blocked tear duct surgery?
Blocked tear duct surgery, or dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), is a procedure that creates a new pathway for tears to drain from the eye into the nose, bypassing the blocked tear duct. This can be achieved through an external DCR or an endoscopic DCR.
What are the risks of blocked tear duct surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with blocked tear duct surgery, including bleeding, infection, and displacement of the tube used to keep the new duct open.
Further Information on the Service
Causes of Blocked Tear Ducts
Blocked tear ducts can be caused by a variety of health problems, including anatomical issues present at birth, chronic nasal and sinus inflammation, obstruction from a tumour, trauma to the nose, or conjunctivitis.
Conditions Warranting Blocked Tear Duct Surgery
Blocked tear duct surgery is typically recommended when less invasive treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, or if the symptoms are severe. These symptoms can include excessive tearing, discharge, and increased susceptibility to eye infections.
Related Concerns
Blocked tear ducts can lead to a variety of complications, including chronic eye infections, inflammation of the tear sac (dacryocystitis), and an increased risk of eye injuries due to impaired vision from excessive tearing.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for blocked tear ducts can range from non-surgical interventions such as warm compresses, massage, and antibiotics, to surgical procedures like dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR). The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause of the blockage.
Alternatives to Surgery
Non-surgical treatment options for blocked tear ducts include warm compresses, massage, antibiotics for infection, and dilation of the nasolacrimal duct. However, if these treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, or if the symptoms are severe, surgery may be necessary.
Service Overview
Blocked tear duct surgery, or dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), involves creating a new pathway for tears to drain from the eye into the nose, bypassing the blocked tear duct. This can be achieved through an external DCR, where a small incision is made on the side of the nose, or an endoscopic DCR, performed through the nose without leaving a skin incision.
Benefits and Risks of Blocked Tear Duct Surgery
The primary benefit of blocked tear duct surgery is the alleviation of symptoms such as excessive tearing and discharge. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are risks, including bleeding, infection, and displacement of the tube used to keep the new duct open.
Preparation for Surgery
Prior to surgery, patients may need to undergo tests to confirm the blockage and its location. Patients may also be advised to stop taking certain medications that can increase the risk of bleeding.
Pre-surgery Procedures and Checks
On the day of surgery, patients will undergo final checks to confirm their health status and the details of the procedure. This may include a review of the patient's medical history and a physical examination.
Step-by-Step Guide to Blocked Tear Duct Surgery
- The patient is given general or local anaesthesia.
- A small incision is made on the side of the nose (external DCR) or inside the nose (endoscopic DCR).
- A new passage is created for tears to drain from the eye into the nose.
- A temporary, flexible tube is placed to keep the new duct open as it heals.
- The incision is closed with stitches. ### Postoperative Care After surgery, patients may be prescribed eye drops and a nasal spray to aid healing. The stitches and the temporary tube are usually removed in a follow-up appointment. ### Recovery and Rehabilitation Recovery from blocked tear duct surgery is typically comfortable, with minor bruising or swelling resolving over the first few weeks. Most patients notice a decrease in tearing and discharge after the procedure. ## References
- "Information for Patients on Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)" - www.hey.nhs.uk
- "Dacryocystorhinostomy: Treatment for a Blocked Tear Duct" - www.hopkinsmedicine.org
- "Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) - Ophthalmic Consultants of Vermont" - www.ocvermont.com
- "Blocked tear duct-Blocked tear duct - Diagnosis & treatment - Mayo Clinic" - www.mayoclinic.org
- "Endoscopic Tear Duct Surgery" - www.opsga.com
Ask your doctor to refer you onto Odycy
Book Online DoctorGet A Referral
Some services need a referral. Ask your doctor to refer you onto Odycy. You can also upload one or get a referral quickly online or phone:
Get A Referral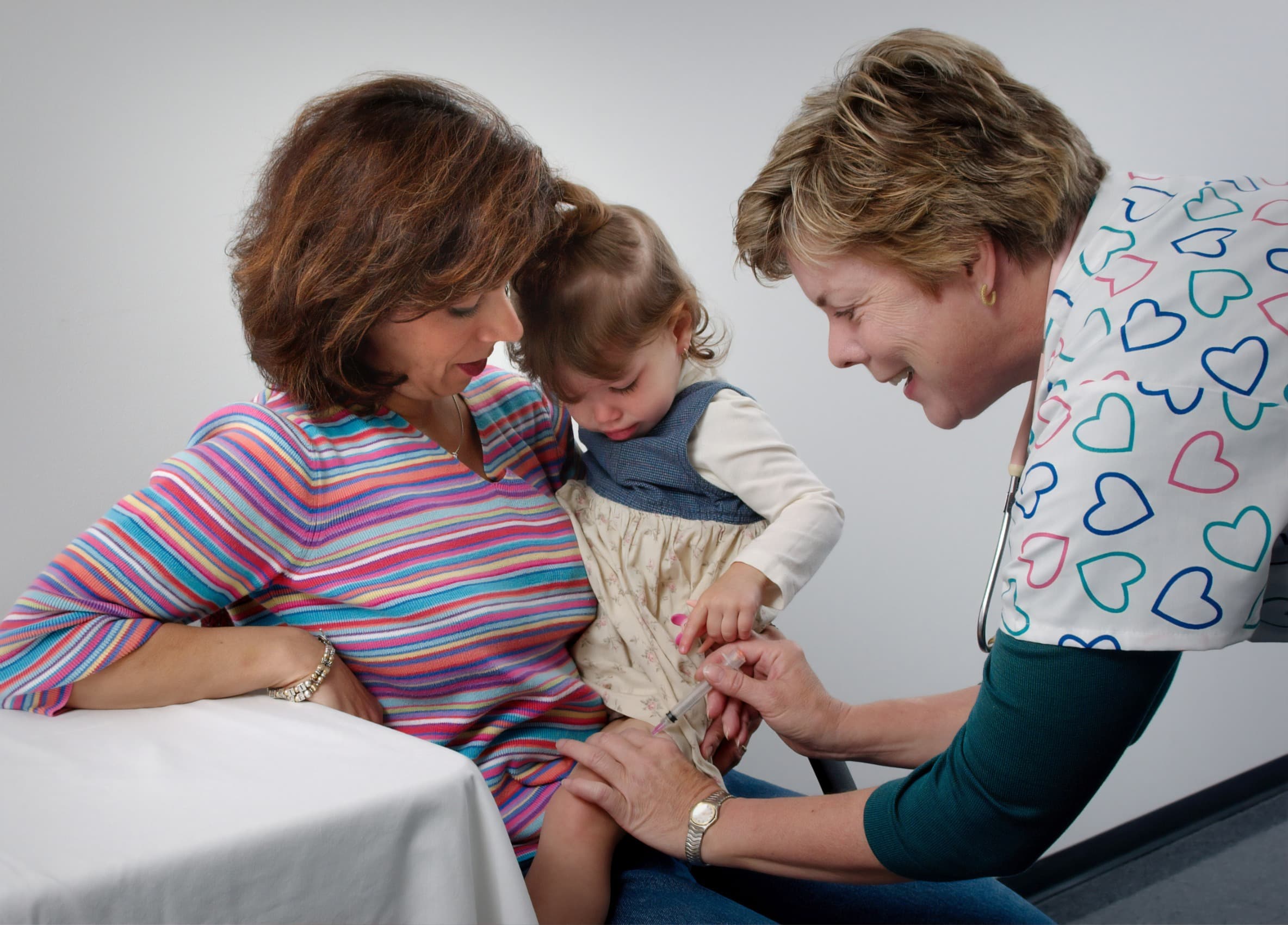
Discuss Results
Talk To A DoctorOdycy is a platform established by a team of experienced doctors and healthcare professionals dedicated to delivering professional, transparent, and dependable health information. Our mission is to empower patients by providing them with comprehensive resources to find, compare and book the highest quality healthcare services according to their individual needs. Our content is periodically reviewed by a panel of expert doctors, researchers, and editors. This rigorous review process ensures that the information we provide is accurate, current, and trustworthy, allowing you to make informed healthcare decisions with confidence. Read about Our Editorial Team and Our Editorial Guidelines.