Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery
Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery treats fluid accumulation in children.
Find, compare and book Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery from the best Private Provider near you. Search for Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery or select from the menu, and book Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery online now.
Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery
Understanding Hydrocele
A hydrocele is a type of scrotal swelling that occurs when fluid accumulates in the thin sheath surrounding a testicle. It's most common in newborns, but it can also occur at any age in later life. While usually painless, large hydroceles can cause discomfort due to their size.
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
Hydrocele repair surgery, or hydrocelectomy, becomes necessary when the hydrocele is large, causing discomfort, or when it doesn't disappear on its own, especially in children over 1 year old. In adults, surgery may be recommended if the hydrocele causes discomfort or if it's associated with an inguinal hernia or testicular torsion.
Overview of the Surgical Procedure
Hydrocele repair surgery involves making a small incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen to drain the fluid and repair the opening through which the fluid has accumulated. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour.
Book Now

Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery
Paediatric Hydrocele Repair Surgery
Key takeways
- Hydrocele repair surgery is a safe and effective treatment for hydroceles that are large, causing discomfort, or not disappearing on their own.
- The surgery provides immediate relief from discomfort and prevents potential complications.
- Preparation for surgery includes fasting and discussing medications with the surgeon.
- Postoperative care involves pain management, wound care, and activity restrictions.
- Recovery is typically quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a week.
- Alternatives to surgery include watchful waiting and needle aspiration, but these have higher recurrence rates.
Common Symptoms and Conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a hydrocele?
A hydrocele is a type of scrotal swelling that occurs when fluid accumulates in the thin sheath surrounding a testicle.
What causes a hydrocele?
Hydroceles are often caused by an imbalance in the production or absorption of fluid, or by a blockage in the spermatic cord.
How is a hydrocele treated?
Treatment options for hydrocele include watchful waiting, needle aspiration, and surgery.
What does hydrocele repair surgery involve?
The surgery involves making a small incision in the scrotum or lower abdomen to drain the fluid and repair the opening through which the fluid has accumulated.
What are the risks of hydrocele repair surgery?
Potential risks include infection, bleeding, injury to the testicle or spermatic cord, and hydrocele recurrence.
Further Information on the Service
Related Concerns
If left untreated, hydroceles can lead to complications such as inguinal hernia, infection, or shrinkage of the testicles. In rare cases, a hydrocele may also be associated with testicular cancer.
Causes of the Issues
Hydroceles are often caused by an imbalance in the production or absorption of fluid, or by a blockage in the spermatic cord. In infants, hydroceles can occur when the opening between the abdomen and the scrotum doesn't close properly after birth.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for hydrocele include watchful waiting, needle aspiration, and surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the patient's age, the size of the hydrocele, and the presence of other conditions.
Service Overview
Hydrocele repair surgery is a safe and effective treatment for hydrocele. It provides immediate relief from symptoms and prevents complications. The surgery can be performed using open or laparoscopic techniques, depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's preference.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hydrocele Repair Surgery
- The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- A small incision is made in the scrotum or lower abdomen.
- The fluid is drained from the hydrocele sac.
- The opening in the sac is repaired to prevent fluid accumulation.
- The incision is closed with stitches. ### Conditions Warranting Hydrocele Repair Surgery Hydrocele repair surgery is recommended in cases where the hydrocele is large, causing discomfort, or not disappearing on its own, especially in children over 1 year old. Lifestyle considerations such as physical discomfort during activities or psychological distress due to the appearance of the swelling may also warrant the surgery. ### Benefits of Hydrocele Repair Surgery The surgery provides immediate relief from discomfort and prevents potential complications such as inguinal hernia or infection. It also improves the appearance of the scrotum, which can enhance the patient's self-esteem and quality of life. ### Risks of Hydrocele Repair Surgery While generally safe, the surgery carries potential risks such as infection, bleeding, injury to the testicle or spermatic cord, and the possibility of hydrocele recurrence. ### Preparation for Surgery Patients are usually advised to fast for several hours before the surgery. Any medications or supplements should be discussed with the surgeon, as some may need to be stopped temporarily. ### Pre-surgery Procedures and Checks At the hospital, vital signs are checked, and the surgical area is cleaned. An IV line is inserted for administering medications and fluids. ### Postoperative Care After surgery, patients are monitored until the anesthesia wears off. Pain medication is provided, and instructions for wound care and activity restrictions are given. ### Recovery and Rehabilitation Recovery is typically quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a week. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor healing and detect any potential complications early. ### Alternatives to Surgery In some cases, a hydrocele may be treated non-surgically through watchful waiting or needle aspiration. However, these methods have higher recurrence rates and are less commonly recommended. ## References
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Hydrocele. [online] Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hydrocele/symptoms-causes/syc-20363969 [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
- NHS. (2023). Hydrocele in adults. [online] Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hydrocele-in-adults/ [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Hydrocele Repair. [online] Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17506-hydrocele-repair [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
- MedlinePlus. (2023). Hydrocele. [online] Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000518.htm [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
- American Urological Association. (2023). Pediatric Hydrocele and Hernia. [online] Available at: https://www.auanet.org/guidelines/pediatric-hydrocele-and-hernia [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
- Urology Care Foundation. (2023). What is Hydrocele? [online] Available at: https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/h/hydrocele [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
- British Association of Urological Surgeons. (2023). Hydrocele Repair. [online] Available at: https://www.baus.org.uk/_userfiles/pages/files/Patients/Leaflets/Hydrocele.pdf [Accessed 8 Dec. 2023].
Ask your doctor to refer you onto Odycy
Book Online DoctorGet A Referral
Some services need a referral. Ask your doctor to refer you onto Odycy. You can also upload one or get a referral quickly online or phone:
Get A Referral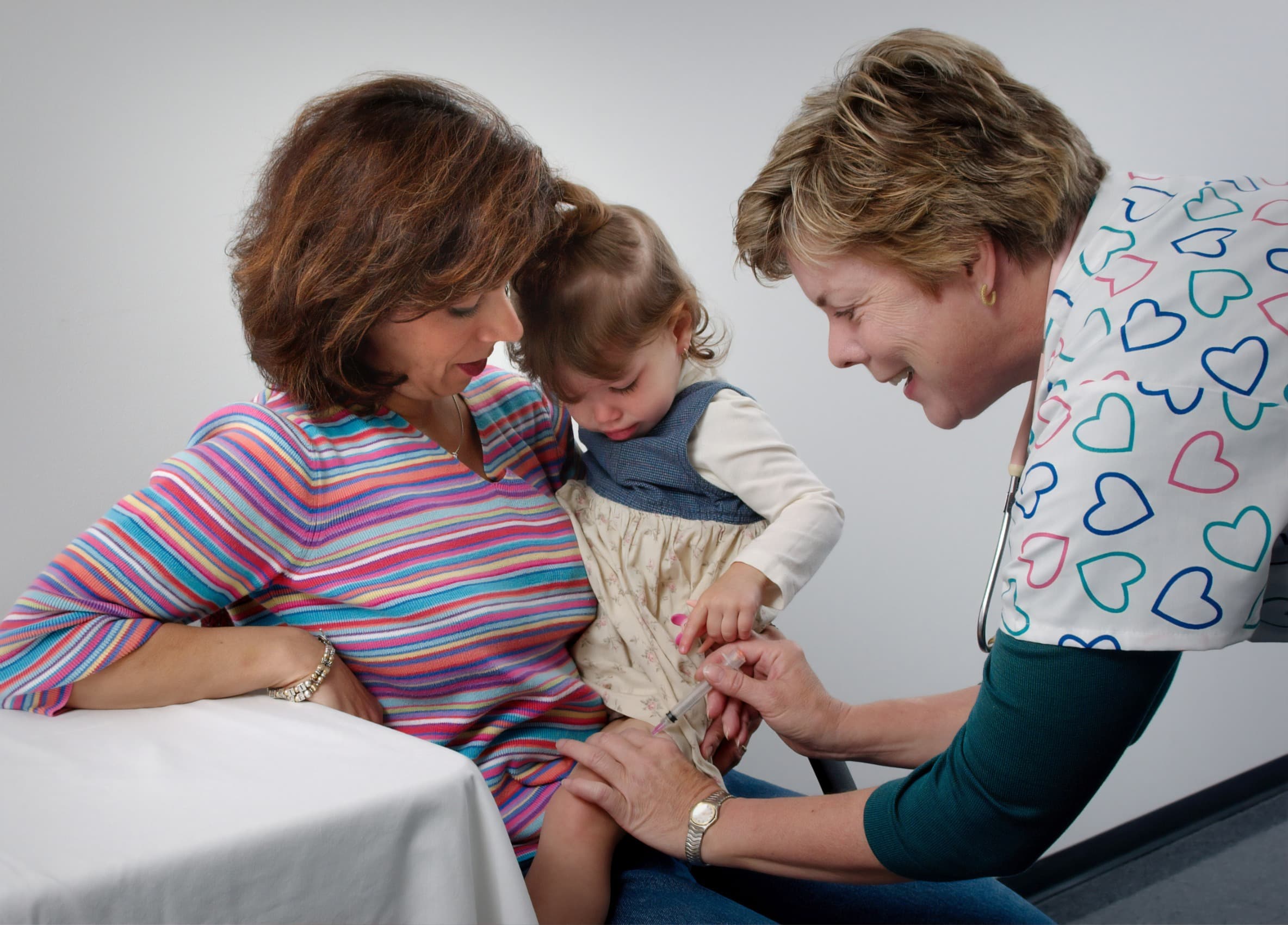
Discuss Results
Talk To A DoctorOdycy is a platform established by a team of experienced doctors and healthcare professionals dedicated to delivering professional, transparent, and dependable health information. Our mission is to empower patients by providing them with comprehensive resources to find, compare and book the highest quality healthcare services according to their individual needs. Our content is periodically reviewed by a panel of expert doctors, researchers, and editors. This rigorous review process ensures that the information we provide is accurate, current, and trustworthy, allowing you to make informed healthcare decisions with confidence. Read about Our Editorial Team and Our Editorial Guidelines.