Middle Ear Surgery
Repairs ear drum damage to improve hearing and reduce infections.
Find, compare and book Middle Ear Surgery from the best Private Provider near you. Search for Middle Ear Surgery or select from the menu, and book Middle Ear Surgery online now.
Middle Ear Surgery
Understanding the Middle Ear
The middle ear is a crucial part of our auditory system, comprising the tympanic membrane (eardrum), ossicles (small bones), mastoid, and eustachian tube. It plays a significant role in amplifying and conducting sound vibrations from the outer ear to the inner ear.
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
Middle ear surgery becomes necessary when conditions such as large eardrum perforations or chronic middle ear infections, like otitis media, do not respond to antibiotics. Other conditions that may necessitate surgery include abnormal skin growth in the middle ear (cholesteatoma) and damage to the ossicles due to infection or trauma.
Overview of the Surgical Procedure
Middle ear surgery, or tympanoplasty, involves the use of a laser to remove excess tissue or scarring in the middle ear. A small piece of tissue is then grafted from a vein or muscle sheath onto the eardrum. The procedure typically takes two to three hours and is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital.
Book Now

Middle Ear Surgery
Middle Ear Surgery
Key takeways
- Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure used to treat conditions such as chronic otitis media, large eardrum perforations, and cholesteatoma.
- The surgery can restore hearing, reduce the frequency of ear infections, and alleviate symptoms such as ear pain and discharge.
- Risks of tympanoplasty include infection, bleeding, changes in taste, facial nerve injury, and persistent or worsened hearing loss.
- Recovery from tympanoplasty typically takes a few weeks, and patients may need to avoid certain activities during this time.
Common Symptoms and Conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Tympanoplasty?
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure used to treat conditions of the middle ear, such as chronic otitis media, large eardrum perforations, and cholesteatoma. The surgery involves removing any infection or dead tissue in the eardrum and placing a graft to reconstruct the tympanic membrane.
What conditions warrant Tympanoplasty?
Tympanoplasty is recommended for conditions such as chronic otitis media, large eardrum perforations, and cholesteatoma. These conditions can cause symptoms like hearing loss, ear pain, and recurrent infections.
What are the benefits of Tympanoplasty?
Tympanoplasty can restore hearing, reduce the frequency of ear infections, and alleviate symptoms such as ear pain and discharge. It can also prevent serious complications associated with chronic middle ear conditions.
What are the risks of Tympanoplasty?
Risks of tympanoplasty include infection, bleeding, changes in taste, facial nerve injury, and persistent or worsened hearing loss. There's also a chance that the surgery might not fully restore hearing or that the eardrum graft might not heal properly.
How should I prepare for Tympanoplasty?
Before surgery, inform your doctor about any medications and supplements you are taking, as well as any known allergies. Avoid eating and drinking the night before and the morning of the surgery.
What does postoperative care involve?
After surgery, the ear will be packed and bandaged to protect it. You will receive instructions on how to care for the surgical site at home, including when to change dressings and how to identify signs of infection.
What is the recovery and rehabilitation process like?
Recovery from tympanoplasty typically takes a few weeks. You may be advised to avoid certain activities, such as swimming and heavy lifting, during this time. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor healing and assess hearing improvement.
Are there alternatives to Tympanoplasty?
Non-surgical treatment options for middle ear conditions include antibiotics for infections and hearing aids for hearing loss. However, these treatments may not be effective for all patients or all types of middle ear conditions.
Further Information on the Service
Related Concerns
Middle ear conditions that may necessitate surgery include eardrum perforations, chronic otitis media, and cholesteatoma. These conditions can lead to symptoms such as hearing loss, drainage, and pain.
Causes of the Issues
These conditions can be caused by various factors, including infections, trauma to the ear, or abnormal growths in the middle ear.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for middle ear conditions include antibiotics for infections, and surgical procedures such as myringoplasty, ossiculoplasty, and tympanoplasty for more severe cases.
Service Overview
Tympanoplasty is a suitable solution for large eardrum perforations or chronic middle ear infections that do not respond to antibiotics. The procedure involves removing any infection or dead tissue in the eardrum and placing a graft to reconstruct the tympanic membrane.
Step-by-Step Guide to Tympanoplasty
- The surgeon accesses the middle ear through a cut behind the ear or through the ear canal.
- Any infection or dead tissue in the eardrum is removed.
- A graft is placed to reconstruct the tympanic membrane. ### Conditions Warranting Tympanoplasty Tympanoplasty is recommended for conditions such as chronic otitis media, large eardrum perforations, and cholesteatoma. These conditions can significantly affect a person's quality of life, causing symptoms like hearing loss, ear pain, and recurrent infections. Lifestyle considerations, such as occupation or hobbies that involve exposure to loud noises, may also influence the decision to undergo tympanoplasty. ### Benefits of Tympanoplasty Tympanoplasty can restore hearing, reduce the frequency of ear infections, and alleviate symptoms such as ear pain and discharge. It can also prevent the development of serious complications associated with chronic middle ear conditions, such as mastoiditis and meningitis. ### Risks of Tympanoplasty Like any surgical procedure, tympanoplasty carries some risks. These include infection, bleeding, changes in taste, facial nerve injury, and persistent or worsened hearing loss. There's also a chance that the surgery might not fully restore hearing or that the eardrum graft might not heal properly. ### Preparation for Surgery Before surgery, patients should inform their doctor about any medications and supplements they are taking, as well as any known allergies. They should also avoid eating and drinking the night before and the morning of the surgery. ### Pre-surgery Procedures and Checks On the day of the surgery, patients will undergo a final check of their medical history and current health status. This may include blood tests and a physical examination. ### Postoperative Care After surgery, the ear will be packed and bandaged to protect it. Patients will receive instructions on how to care for the surgical site at home, including when to change dressings and how to identify signs of infection. ### Recovery and Rehabilitation Recovery from tympanoplasty typically takes a few weeks. Patients may be advised to avoid certain activities, such as swimming and heavy lifting, during this time. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor healing and assess hearing improvement. ### Alternatives to Surgery Non-surgical treatment options for middle ear conditions include antibiotics for infections and hearing aids for hearing loss. However, these treatments may not be effective for all patients or all types of middle ear conditions. ## References
- Albany ENT & Allergy Services. (2021). What You Need to Know About Middle Ear Surgery. https://albanyentandallergy.com/what-you-need-to-know-about-middle-ear-surgery/
- MedicineNet. (2023). What Is Middle Ear Surgery? 4 Types, Causes & Is It Safe? https://www.medicinenet.com/what_is_middle_ear_surgery/article.htm
- ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). Middle Ear Surgery. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/middle-ear-surgery
- Top Doctors. (2023). Middle ear surgery: What is it and what's involved? https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/medical-dictionary/middle-ear-surgery
- PubMed. (2023). Introduction to the surgery of the middle ear: general principles. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8129965/
Ask your doctor to refer you onto Odycy
Book Online DoctorGet A Referral
Some services need a referral. Ask your doctor to refer you onto Odycy. You can also upload one or get a referral quickly online or phone:
Get A Referral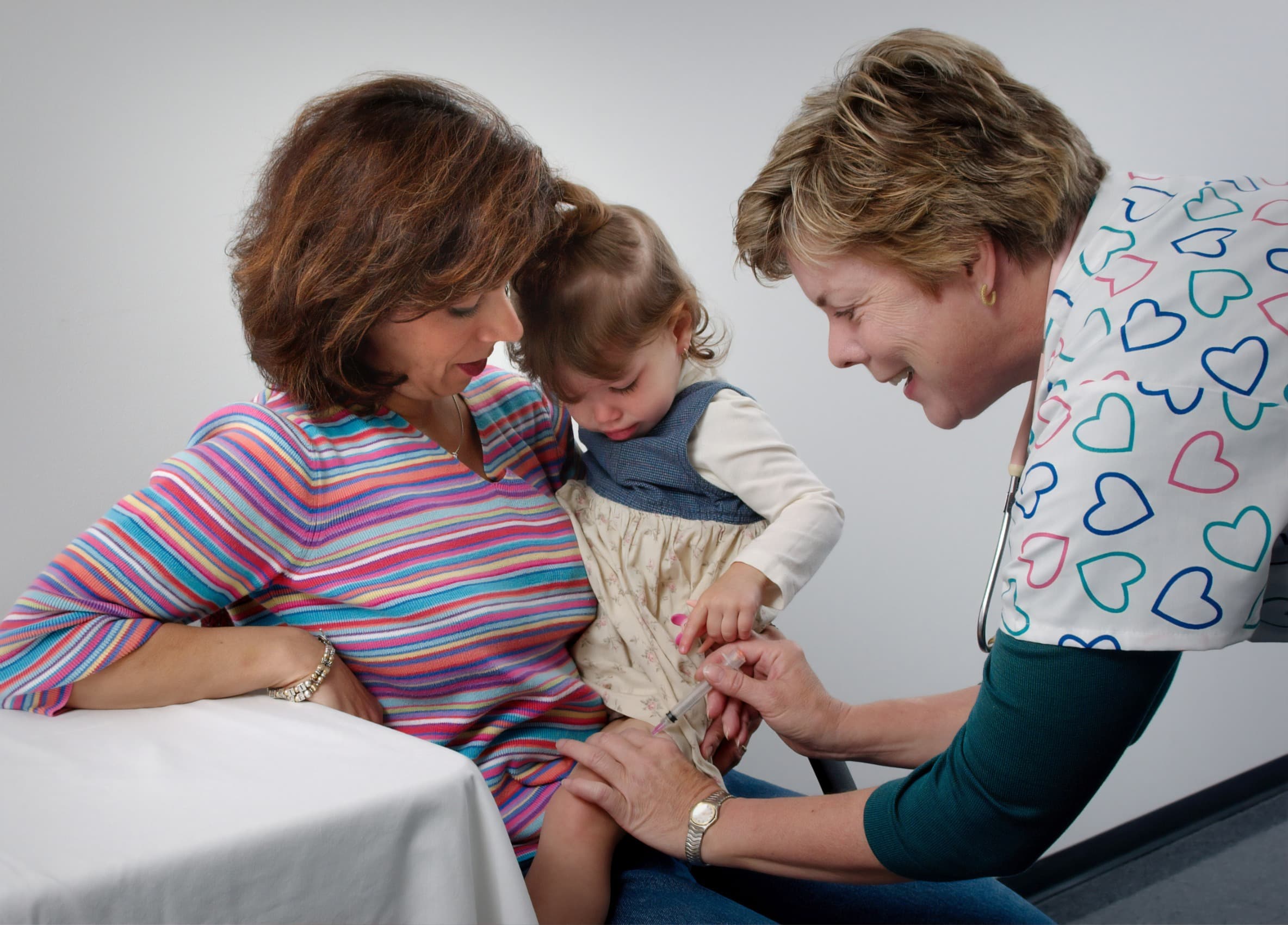
Discuss Results
Talk To A DoctorOdycy is a platform established by a team of experienced doctors and healthcare professionals dedicated to delivering professional, transparent, and dependable health information. Our mission is to empower patients by providing them with comprehensive resources to find, compare and book the highest quality healthcare services according to their individual needs. Our content is periodically reviewed by a panel of expert doctors, researchers, and editors. This rigorous review process ensures that the information we provide is accurate, current, and trustworthy, allowing you to make informed healthcare decisions with confidence. Read about Our Editorial Team and Our Editorial Guidelines.